(January 12, 2016) Researchers
in Germany studied how a multitude of electronic interactions govern the
encounter between a molecule called porphine and copper and silver surfaces
As we continue to shrink electronic components, top-down
manufacturing methods begin to approach a physical limit at the nanoscale.
Rather than continue to chip away at this limit, one solution of interest
involves using the bottom-up self-assembly of molecular building blocks to
build nanoscale devices.
Successful self-assembly is an elaborately choreographed
dance, in which the attractive and repulsive forces within molecules, between
each molecule and its neighbors, and between molecules and the surface that
supports them, have to all be taken into account. To better understand the
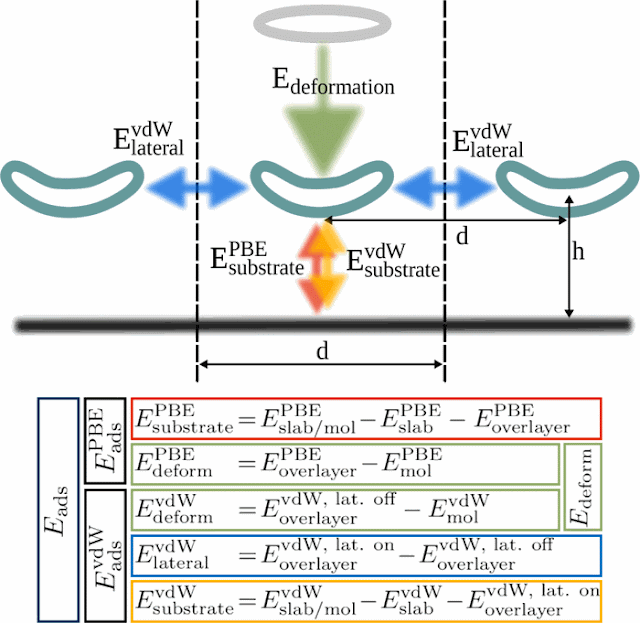
self-assembly process, researchers at the Technical University of Munich have
characterized the contributions of all interaction components, such as covalent
bonding and van der Waals interactions between molecules and between molecules
and a surface.
“In an ideal case, the smallest possible device has the size
of a single atom or molecule,” said Katharina Diller, who worked as a
postdoctoral researcher in the group of Karsten Reuter at the Technical
University of Munich. Reuter and his colleagues present their work this week in
The Journal of Chemical Physics, from AIP Publishing.
One such example is a single-porphyrin switch, which
occupies a surface area of only one square nanometer. The porphine molecule,
which was the object of this study, is even smaller than this. Porphyrins are a
group of ringed chemical compounds which notably include heme – responsible for
transporting oxygen and carbon dioxide in the bloodstream – and chlorophyll. In
synthetically-derived applications, porphyrins are studied for their potential
uses as sensors, light-sensitive dyes in organic solar cells, and molecular
magnets.